How to Differentiate a Mastodon from a Dinosaur: A Quick Guide
Mastodons had conical, nipple-like teeth, whereas dinosaurs possessed varied teeth shapes. Mastodons are ancient mammals, while dinosaurs were reptiles.
Distinguishing between mastodons and dinosaurs can be surprisingly straightforward with the right information.
Mastodons belonged to a group of prehistoric animals known as proboscideans, which includes modern-day elephants.
These creatures roamed the earth during the late Miocene to the Holocene epoch, becoming extinct approximately 11,000 years ago.
Unlike dinosaurs, mastodons were a part of the Cenozoic Era’s vast mammalian megafauna. Their most distinctive feature was their teeth, adapted for chewing leaves and branches, unlike the often sharp and pointed teeth of dinosaurs used for tearing meat or grinding plant matter.
Dinosaurs, existing from the Triassic to the Cretaceous periods, showcased a vast array of characteristics across numerous species.
From the ferocious Tyrannosaurus rex to the towering Brachiosaurus, dinosaurs were an incredibly diverse group that dominated the Mesozoic Era’s landscapes for over 160 million years before going extinct 65 million years ago.
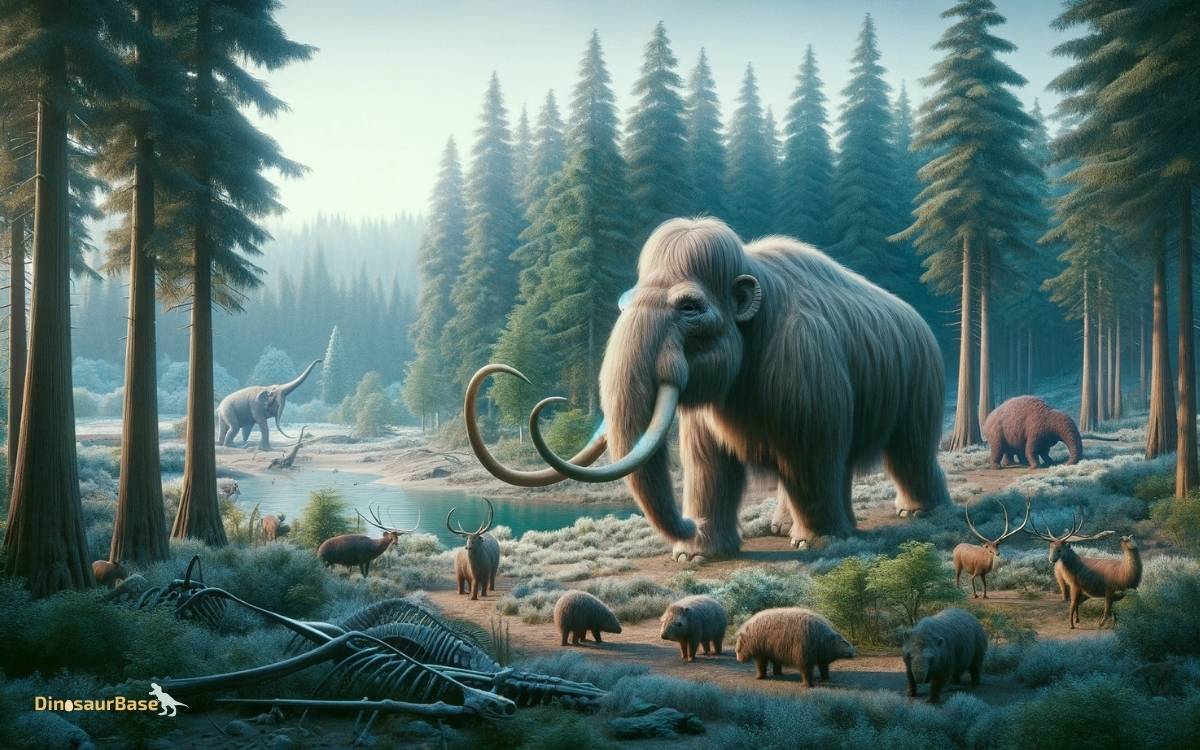

The Rise Of The Mastodons Vs. The Age Of Dinosaurs
When we dive into the history of Earth’s magnificent creatures, two giants stand out: mastodons and dinosaurs.
Though they both roamed vast landscapes and have captured our imaginations, they existed in different times and had distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Let’s embark on a journey to understand these ancient animals, and how to differentiate a mastodon from a dinosaur.
Eras Of Existence
Dinosaurs ruled long before mastodons appeared on Earth. To put their timelines in perspective, let’s explore their eras:
- Dinosaurs: Dominated the Mesozoic Era, which spanned from about 252 to 66 million years ago.
- Mastodons: Emerged much later, thriving from about 27 to 0.011 million years ago, in the Cenozoic Era.
We can visualize these eras like chapters in a book:
| Chapter (Era) | Dinosaurs | Mastodons |
|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic | 252 – 66 million years ago | – |
| Cenozoic | – | 27 – 0.011 million years ago |
This simple table clarifies that the two did not share the same time period.
Distinct Lineages
Mastodons and dinosaurs stem from very different ancestral trees. Their lineages paint a picture of their unique backgrounds:
- Dinosaurs: Belong to Reptilia, alongside lizards and snakes.
- Mastodons: Part of Mammalia, related to modern elephants.
Looking at their family trees, we notice distinct roots:
| Family Tree | Dinosaurs | Mastodons |
|---|---|---|
| Classification | Reptilia | Mammalia |
| Close Relatives | Lizards, Birds | Elephants |
This separation illustrates why dinosaurs and mastodons are not as closely related as some might think.
Understanding the rise of mastodons and the age of dinosaurs reveals a staggering timeline of life on Earth. With this guide, one can easily differentiate these prehistoric giants by their eras of existence and distinct ancestries. Remembering these facts ensures you never confuse a mastodon for a dinosaur again.

Credit: earthathome.org
Key Physical Traits Of Mastodons
Understanding the key physical traits of mastodons helps us spot the differences with dinosaurs.
Though both ancient creatures, mastodons roamed Earth much later. Their characteristics are fascinating and distinct.
Ivory Tusks And Molars
Mastodons had long, curved ivory tusks, sometimes reaching over 5 meters. Their tusks give clues about their habits. Mastodons used them for defense and foraging in the forest.
- Tusks: Welcome tools for lifting objects or stripping bark.
- Molars: High ridges and cusps on their teeth ground down plant material. Their molars tell us they ate leaves and twigs.
Body Structure And Size Comparison
Mastodons were stocky and muscular, typically shorter than today’s elephants. With thick, shaggy hair, they were well-suited for cold climates. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Mastodon | Dinosaur (Avg. Sauropod) |
|---|---|
| Height: 2.5 meters | Height: 15-20 meters |
| Weight: 6 tons | Weight: Up to 90 tons |
| Body: Short limbs, barrel chest | Body: Long neck and tail, massive legs |
The size and body build of mastodons was unique. Comparing to dinosaurs, they were more compact. Their features equipped them well for their environment. A quick glance at the stats above highlights stark contrasts.
Anatomical Differences In Dinosaurs
Understanding the anatomical variations of dinosaurs is key to differentiating these ancient creatures.
Diverse body structures and unique features characterized each species.
By examining these differences, it’s possible to paint a vivid picture of how each dinosaur may have lived.
Diverse Dinosaur Clades
Dinosaurs were not a homogenous group; they were split into various clades, or groups.
Each clade had distinct anatomical traits that suited different lifestyles.
Among the broadest classifications are the Ornithischia, known for bird-like hips, and the Saurischia, with lizard-like hips.
- Sauropodomorpha: Long-necked giants like Brachiosaurus.
- Theropoda: Carnivorous bipeds, including Tyrannosaurus rex.
- Cerapoda: Triceratops and other herbivores.
Variations In Size And Form
Dinosaurs displayed incredible variation in size and shape. Some were as small as chickens, while others towered over buildings.
| Size Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Small | Compsognathus, Velociraptor |
| Medium | Iguanodon, Allosaurus |
| Large | Brontosaurus, Spinosaurus |
Form also varied greatly between species, from the spike-tailed Stegosaurus to the armored Ankylosaurus.
The diversity in limb structure, skull shape, and tail design served various functions from defense to feeding.
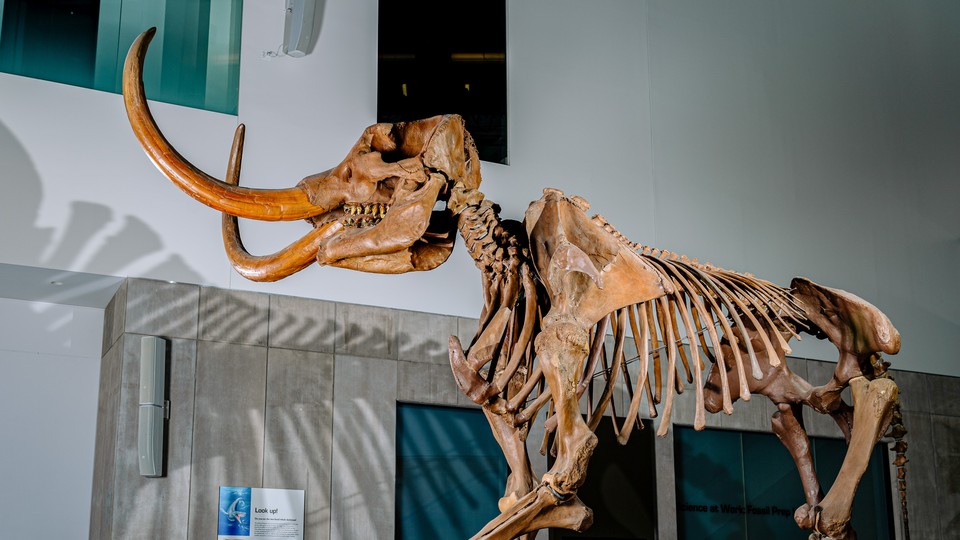

Credit: www.theatlantic.com
Habitats: Where Mastodons And Dinosaurs Roamed
Understanding the habitats of ancient creatures tells us much about their lives. Mastodons and dinosaurs lived in different times and places.
Let’s travel back in time and explore these ancient habitats.
Mastodons in Ice Age Landscapes
Mastodons In Ice Age Landscapes
Mastodons thrived during the Ice Age. This period was known for its glacial landscapes. Vast frozen expanses and coniferous forests formed the stomping grounds of these prehistoric giants.
- North America and Eurasia were prime mastodon habitats.
- They traversed cold, swampy areas, dense with vegetation.
- Mastodons were browsers, eating shrubs and trees suited to their chilly environments.
Dinosaurs Across Ancient Terrains
Dinosaurs Across Ancient Terrains
Dinosaurs dominated a range of habitats. From lush jungles to arid deserts, they left footprints across the globe during the Mesozoic Era.
| Period | Habitat Characteristics | Common Dinosaurs |
|---|---|---|
| Triassic | Dry interiors, large riverside forests | Coelophysis, Plateosaurus |
| Jurassic | Vast plains, coniferous forests | Stegosaurus, Allosaurus |
| Cretaceous | Coastal plains, tropical climates | Tyrannosaurus, Triceratops |
The Fossil Record: Unearthing Clues
Imagine, for a moment, being a detective with a time machine. Now imagine that your case involves solving the mystery of creatures that lived millions of years ago. Welcome to the world of paleontology, where fossil records provide vital evidence.
These ancient remnants offer insights into how mastodons and dinosaurs lived and, more importantly, how to tell them apart. Let’s dig into the clues that fossils provide.
Deciphering Fossilized Remains
Uncovering a fossil is just the beginning. Scientists look at features like bone structure, teeth, and patterns in the fossil to tell a story.
Mastodons, for example, have spiral-tusked remains and molar patterns distinct from any dinosaur.
These pieces come together like a jigsaw puzzle, providing a clear image of the creature they belong to.
- Bone Structure: Mastodon bones are generally less massive than those of many dinosaurs.
- Teeth: Mastodon teeth have ridges perfect for grinding vegetation.
- Fossil Patterns: The environment where the fossils are found also hints at the creature’s identity.
Dating Techniques And Discoveries
Determining when a creature lived is crucial. Experts use methods like radiocarbon dating to measure the age of fossils.
This technique can pinpoint the time period a mastodon walked the Earth, distinctly after the time of dinosaurs, which is confirmed through other dating strategies.
| Fossil Type | Dating Technique | Time Period Identified |
|---|---|---|
| Mastodon | Radiocarbon | Pleistocene Epoch |
| Dinosaur | Uranium-Lead | Mesozoic Era |
Key discoveries further strengthen these findings:
- First mastodon fossils found in North America.
- Dinosaur fossils emerge from layers way beneath mastodon findings.
- Diverse locations of dinosaur discoveries show they roamed vast areas.

Credit: www.nps.gov
Cultural And Popular Perceptions
Cultural and popular perceptions shape our understanding of prehistoric creatures. The mastodon and the dinosaur, both giants of the past, often get tangled in a web of myths and media representations. This quick guide invites you to journey through time to unravel these mix-ups.
Misconceptions And Myths
Common misconceptions can cast a shadow over the true identity of the mastodon. Unlike their dinosaur cousins, mastodons roamed the Earth during the Ice Age, a much later era. Let’s bust some myths:
- Mastodons are dinosaurs: False. Mastodons are prehistoric mammals, not dinosaurs.
- All giant fossils are dinosaurs: Incorrect. Fossil size doesn’t determine dinosaur status.
- Mastodons and mammoths are the same: No, they differ in tooth structure and other features.
Educational Impact And Media Representations
The media often showcases mastodons alongside dinosaurs, leading to confusion. Accurate educational content can help differentiate the two:
| Mastodon | Dinosaur |
|---|---|
| Cenozoic era | Mesozoic era |
| Mammal | Reptile |
| Fur-covered | Scales or feathers |
Television shows, movies, and books often lump these creatures together. Educators and creators must portray these prehistoric beasts accurately to foster knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions Of How To Differentiate A Mastodon From A Dinosaur: A Quick Guide
Is A Mastodon Considered A Dinosaur?
No, a mastodon is not a dinosaur. Mastodons were prehistoric relatives of elephants, living after the dinosaurs went extinct.
What Does A Prehistoric Mastodon Look Like?
A prehistoric mastodon had a thick, shaggy coat, large tusks curving upwards, and a massive body structure resembling a woolly mammoth. Its appearance was robust with a prominent hump on its back.
What Distinguishing Characteristics Did The American Mastodon Have?
The American mastodon had long, curved tusks and a low, ridged back. Its molars bore blunt cones, ideal for chewing foliage.
How Can You Tell The Difference Between A Mammoth And A Mastodon?
Mammoths were generally larger with curved tusks and a hump of fat on their backs. Mastodons had straighter tusks and more muscular builds with flatter backs. Their teeth also differed; mammoths had ridged molars for grazing, while mastodons had cone-shaped molars for browsing.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between mastodons and dinosaurs is fascinating and vital for enthusiasts. Embrace these differences to enhance your paleontological knowledge.
We’ve explored key identifiers that shed light on these ancient creatures. Delve deeper to satisfy your curiosity, and share findings with fellow history buffs.
Remember, understanding the past enriches our present.