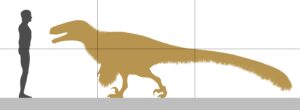
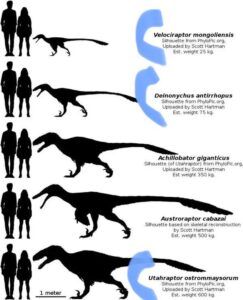
What Was Achillobator’s Habitat in the Late Cretaceous?
Achillobator, a dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period, inhabited what is now Mongolia. Its environment was likely semi-arid with seasonal fluctuations and diverse flora.
The Achillobator, a fierce and captivating creature, roamed the land approximately 90 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous.
Nestled within the expanses of ancient Mongolia, this theropod dinosaur thrived in a habitat characterized by a semi-arid climate.
Scientists suggest that, despite the aridity, the region supported a rich mosaic of vegetation, which in turn sustained a variety of herbivorous dinosaurs – the potential prey for Achillobator.
Researchers base their understanding of Achillobator’s habitat on the fossil evidence excavated from the Bayan Shireh Formation, known for its distinct geological features and ancient faunal remains.
Hence, enthusiasts and academics alike find intrigue in piecing together the lifestyle and environment of this incredible dinosaur, highlighting its prowess as a top predator of its ecosystem.

A Glimpse Into The Cretaceous Period

Credit: dinosaurpictures.org
Step back in time to uncover the world of the formidable Achillobator, a dinosaur that roamed the Earth in the Late Cretaceous.
This period was a vibrant chapter in our planet’s history. Imagine lands ruled by dinosaurs and skies filled with pterosaurs. The Late Cretaceous provides a stunning backdrop for the story of Achillobator’s habitat.
The Timeline Of The Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous epoch occurred around 100.5 to 66 million years ago. During this time, the days on Earth were shorter, and the climate was warmer than today. This era closed the chapter on the age of dinosaurs.
Dinosaurs like the Achillobator lived during this rich timeline. Flowering plants began to diversify, setting the stage for modern ecosystems.
Environmental Characteristics Of The Era
The Late Cretaceous was marked by diverse environments. Tropical conditions prevailed in regions where Achillobator would have lived.
- Forests with tall conifers and flowering plants flouroted.
- Large rivers carved the landscapes.
- Volcanic activity shaped the Earth, creating new habitats.
These habitats supported a vast array of life. Dinosaurs, both large and small, shared this world with mammals, birds, and marine creatures.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Climate | Warm, with high levels of humidity |
| Vegetation | Diverse, ranging from ferns to flowering plants |
| Geography | Continents continued to drift apart |
| Wildlife | Rich diversity, including the fearsome Achillobator |
Achillobator’s habitat was a place of constant change. These beasts adapted to thrive amidst the environmental shifts of their era.
The Realm Of Dinosaurs
Achillobator, a fierce dinosaur, once roamed the earth during the Late Cretaceous period. This era, known as the Realm of Dinosaurs, was a time when these prehistoric creatures dominated the land. Lush forests, wide rivers, and vast plains composed their dynamic habitat.
Diversity Of Dinosaur Species
Dinosaur species were incredibly varied in the Late Cretaceous. Each species had adapted to thrive in specific parts of their environment. Some were small and agile, others towering and robust.
Below is a breakdown of dinosaur categories:
- Theropods: Carnivorous dinosaurs like the Achillobator
- Sauropods: Gigantic herbivores with long necks
- Ornithopods: Plant-eaters, known for running on two legs
- Hadrosaurs: Known as ‘duck-billed dinosaurs’
- Ankylosaurs: Armored dinosaurs with club-like tails
Predators And Prey In The Cretaceous Ecosystem
The food chain played a critical role in the Cretaceous ecosystem. Predators like Achillobator hunted prey to survive. Prey species evolved mechanisms such as speed and armor for protection.
Let’s explore some of the common predator-prey dynamics:
| Predators | Common Prey |
|---|---|
| Achillobator | Small dinosaurs and mammals |
| Tyrannosaurus rex | Hadrosaurs and Triceratops |
| Velociraptor | Protoceratops and small lizards |
Achillobator’s striking features, such as sharp claws and strong legs, suggest it was a formidable hunter.
The environment of the Late Cretaceous provided the perfect backdrop for the drama of survival to unfold, featuring an intricate web of life comprising different dinosaur species, all playing their roles as either predators or prey within their diverse habitats.
Achillobator’s Homeland
Imagine a land teeming with life, where dinosaurs roam. Here, Achillobator, a fierce predator, thrived in the Late Cretaceous.
Geographical Distribution
The Achillobator dinosaur was a resident of what’s now Mongolia. Fossils discovered in the Djadokhta Formation paint a vivid picture of their lives.
This area was the heartland for Achillobator. Scientists have pieced together clues from ancient rocks to map its domain.
Climate Conditions In Achillobator’s Territory
Back then, Mongolia’s landscape was very different. It was not the sandy desert we know today. Instead, it had lush forests and wetlands.
Warm and humid, the habitat was perfect for Achillobator’s survival. Rivers likely crisscrossed the land, supporting a diverse ecosystem.

Credit: dinosaurzus.com
Surviving In Prehistoric Mongolia
The Late Cretaceous period was a time of intense survival. Dinosaurs like Achillobator roamed the land. Mongolia’s landscape offered a unique backdrop for these incredible creatures.
Achillobator, a fearsome dromaeosaurid, was a master of this domain. Let’s explore the flora and fauna of prehistoric Mongolia that Achillobator called home.
Flora: Feeding Ground For Giants
Lush vegetation covered the ancient Mongolian terrain. The habitat was filled with a variety of plants. These ranged from conifers to broadleaf trees.
Mongolia’s vast forestlands were essential to the ecosystem. They provided nourishment for plant-eating dinosaurs.
In turn, those herbivores were prey for predators like Achillobator. The plant life in the area included:
- Ferns
- Ginkgoes
- Cycads
- Angiosperms
Fauna: The Competition For Survival
Predators and prey were locked in a constant battle for survival. The food chain was complex. Achillobator was a top hunter.
Yet, it faced competition from other large carnivores. These included relatives like Velociraptor. Smaller mammals, lizards, and insects filled out the food web.
This balance of species played a crucial role in the ecosystem. Some notable competitors and prey included:
| Competitors | Prey |
|---|---|
| Tarbosaurus | Protoceratops |
| Velociraptor | Oviraptor |
Creatures in the Late Cretaceous period faced extreme challenges. Survival was never guaranteed.
Yet, the rich environment of prehistoric Mongolia allowed species like Achillobator to thrive. This dino was a true survivor of its time.
Unveiling Achillobator’s Niche
Imagine Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous, a place where the Achillobator roamed. This fierce dinosaur lived in a land rich with diverse landscapes. Lush forests, river valleys, and arid deserts made up its world.
Adaptations For Hunting
The Achillobator was a deadly predator. Its physical traits were perfect for the hunt.
- Powerful legs for speed and agility.
- Sharp claws for gripping prey.
- Keen eyesight to spot meals from afar.
These adaptations helped it survive in a competitive habitat.
Interactions With Other Cretaceous Creatures
In its habitat, the Achillobator was not alone. It shared its home with many creatures.
Let’s explore its neighbours:
- Plant-eating giants: A potential prey for the Achillobator.
- Small mammals and reptiles: These also made up part of its diet.
- Rival predators: Competitors for food and territory.
| Type of Creature | Role in Habitat |
|---|---|
| Plant-eaters | Prey |
| Mammals/Reptiles | Food Source |
| Rival Carnivores | Competition for Resources |
Paleontological Insights
The late Cretaceous period was a time of dynamic ecosystems and fascinating creatures, one of which was the remarkable dinosaur known as Achillobator. These magnificent creatures roamed the earth over 90 million years ago.
Unveiling their habitat initiates a journey back in time—guided by the paleontological insights carved from ancient rocks and fossilized remains.
Fossil Evidence And Habitats
The discovery of Achillobator fossils provides insight into their natural world. Fossils suggest they lived in what is now Mongolia.
Geologic formations, such as the Bayan Shireh Formation, have been pivotal in understanding this.
Here’s what the fossil evidence tells us:
- Semi-arid environments with wet and dry seasons.
- Presence of rivers and floodplains, hinting at a water-rich habitat.
- Diverse flora and fauna, indicating a rich food chain.
These factors combined paint a vivid picture of the habitat where the Achillobator thrived.
New Discoveries And Changing Perspectives
As paleontologists unearth more fossils, our understanding of Achillobator’s world evolves. Every new discovery can potentially alter previous perceptions.
Here’s how:
| Year | Discovery | Impact on Habitat Perception |
|---|---|---|
| 1999 | Initial Achillobator fossil found | Confirmed existence in Late Cretaceous Mongolia |
| 2000s | Further fossil fragments unearthed | Clarified the range of ecosystem types |
| 2010s | New data on nearby dinosaur species | Revealed more about potential prey and predators |
With each fossil unearthed and each layer of sediment analyzed, the narrative of the Achillobator’s natural world becomes more detailed. The journey to comprehend their habitat is ongoing, evolving with each exciting discovery.
How Did Achillobator’s Habitat Contribute to its Size Compared to Humans?
Achillobator size comparison to humans reveals the impact of its habitat. The dinosaur lived in an environment with abundant resources and fewer natural predators, allowing it to grow to over 16 feet in length. In contrast, humans have adapted to a wider range of habitats, resulting in smaller average sizes.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Was Achillobator’s Habitat In The Late Cretaceous?
What Was The Habitat Of The Achillobator?
The Achillobator inhabited forested floodplains during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Mongolia.
How Fast Was Achillobator?
The exact speed of Achillobator is unknown, but similar-sized dromaeosaurs likely reached speeds of up to 40 km/h (25 mph).
What Is The Holotype Of The Achillobator?
The holotype of Achillobator is a partial skeleton with the specimen number IGM 100/20. It encompasses various bones, including vertebrae, hindlimb elements, and more.
Is The Deinonychus A Raptor?
Yes, the Deinonychus is a type of raptor, more formally known as a dromaeosaurid, characterized by its agile build and sickle-shaped claw.
Conclusion
Exploring Achillobator’s ancient environment sheds light on the Late Cretaceous era. This fearsome dinosaur roamed vast, lush landscapes. Rich with plant life, these spaces offered ample hunting grounds.
Understanding such habitats deepens our appreciation of Earth’s prehistoric complexity. Remember, the secrets of ages past still influence modern ecosystems.