10 Best Comparisons: Abelisaurus Among Theropod Dinosaurs
Abelisaurus stands out among theropods for its unique skull structure and South American origins. It was a medium-sized carnivore that roamed the Late Cretaceous period.
Abelisaurus, a fascinating member of the theropod dinosaurs, beckons paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike with its distinctive features.
First described in 1985 from fossil remains found in Argentina, Abelisaurus captivates with its unusual, boxy skull shape and a lack of forelimbs, setting it apart from its contemporaries.
As a genus of Abelisauridae, it roams the landscape of scientific discovery, offering insights into the evolution and diversity of predatory dinosaurs.
Understanding Abelisaurus deepens through comparisons with other theropods, shedding light on the adaptations that allowed these creatures to thrive.
While full skeletons remain elusive, the pieces we have paint a picture of a bipedal predator that was an apex hunter in its ecosystem.
Introduction To Abelisaurus
Enter the realm of ancient predators and meet the Abelisaurus, a fascinating dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period.
Abelisaurus roamed the lands of what is now South America. Its name, meaning “Abel’s lizard,” honors the discoverer Roberto Abel.
This carnivorous beast has intrigued scientists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike with its distinctive characteristics and placement within the theropod family tree.
Key Features And Discovery
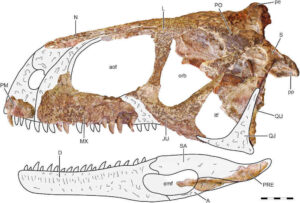
Unearthed in Argentina in 1985, Abelisaurus stands out as a unique theropod. The discovery included only a partial skull, yet it revealed notable features:
- Sizeable Skull: Large head with powerful jaws.
- Short Snout: Unlike relatives with long noses.
- Sharp Teeth: Perfect for a carnivore’s diet.
The skull’s design suggests a keen predator adept at capturing prey.
Abelisaurus In The Theropod Family Tree
Theropods are known for their meat-eating habits and upright stance. Abelisaurus is a part of this diverse group, which includes the famous Tyrannosaurus and Velociraptor.
To understand its place, consider these points:
- Abelisaurus is a ceratosaurian theropod.
- Its closest relatives are noasaurids and carnotaurines.
- Experts use the term abelisaurids to refer to its family.
Each discovery adds a piece to the puzzle of dinosaur evolution, and Abelisaurus is no exception.
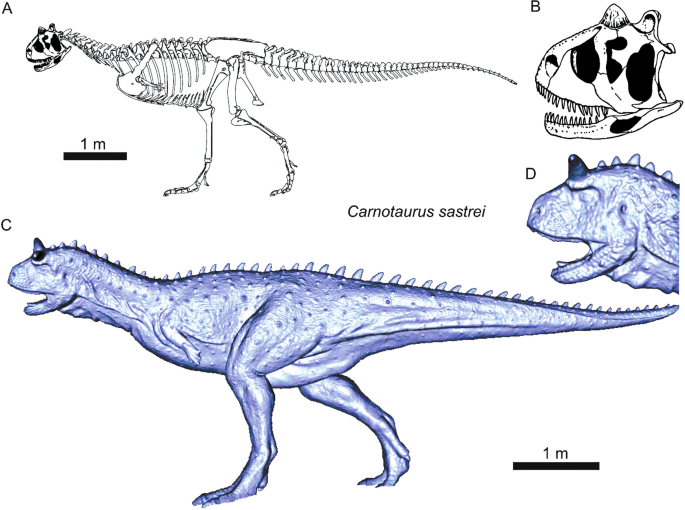
Credit: link.springer.com
Size And Stature
The Abelisaurus, a fierce predator from the Late Cretaceous, holds a unique spot among its theropod relatives.
Size did not only matter for dominance but influenced their ecological roles and survival strategies as well.
Let’s dive into how this dinosaur compared in size to its theropod kin and explore the effects those dimensions had on its behavior.
Comparing dimensions with other theropods
Comparing Dimensions With Other Theropods
The Abelisaurus stands out with a distinct size among the theropod group. While not the largest, its dimensions reveal an intriguing tale of evolution.
A comparative look:
| Theropod | Length (meters) | Height (meters) | Estimated Weight (tons) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abelisaurus | 7-9 | 2.5-3 | 1-2 |
| Tyrannosaurus Rex | 12-13 | 3.5-4 | 7-9 |
| Spinosaurus | 16-18 | 4.5-7 (including sail) | 7-20 |
| Allosaurus | 8.5-12 | 2.5-3.5 | 1.5-2 |
- Abelisaurus was smaller than Tyrannosaurus Rex and Spinosaurus.
- Its size was more comparable to Allosaurus.
Implications of size on ecology and behavior
Implications Of Size On Ecology And Behavior
Size and behavior in dinosaurs are deeply linked. Abelisaurus showcases how size influenced its role in the ecosystem:
- With its smaller stature, Abelisaurus likely relied on quickness and agility.
- It might have targeted smaller prey due to competition from larger theropods.
- Its size could have allowed it to navigate dense forests where larger predators could not go.
These traits reveal a dynamic creature, shaped by its size to adopt unique survival methods in prehistoric times.
Skull Morphology And Diet
Exploring the uniqueness of Abelisaurus opens a fascinating chapter in the story of theropods.
The skull morphology and diet of these ancient creatures offer valuable insights into their daily existence. Let’s delve into how the Abelisaurus’ skull design sets it apart from its theropod relatives.
We’ll also uncover what their teeth and skull structures suggest about their eating habits. The Abelisaurus roamed the earth during the Late Cretaceous period, a time brimming with diverse predatory dinosaurs.
Skull Design Comparison
The skull of Abelisaurus is a marvel to behold in comparison to other theropods. Not as elongated as some, but shorter and robust, it hints at powerful biting. Its distinct features shape its place in the predatory hierarchy.
Below, we examine how it stands out:
- Compact Frame: Unlike the long-snouted forms of theropods like Allosaurus, the Abelisaurus showcases a more compact and deeper skull structure.
- Eye Placement: With forward-facing eyes, Abelisaurus may have had better depth perception, giving it an advantage as a predator.
- Unique Fenestrae: The holes in the skull, or fenestrae, differ in size and shape from others, hinting at distinct muscle attachments and possibly different movement or force of the jaw.
Inferred Diet From Dental And Cranial Anatomy
The teeth and bones around Abelisaurus’s mouth give clues about its diet. Sharp, meat-shearing teeth hint at a carnivorous lifestyle.
Here’s what the dental and cranial anatomy reveal:
| Dental Feature | Inference |
|---|---|
| Teeth Shape | Designed for gripping and tearing flesh, not for grinding plants. |
| Jaw Mechanics | Suggests a powerful bite capable of taking down large prey. |
| Cranial Musculature | Indicates strong neck muscles, useful in a carnivorous lifestyle for tackling struggle-prey. |
In summary, Abelisaurus’s head construction points to a diet dominated by large prey items, requiring robust predatory tactics.

Credit: www.sci.news
Locomotion And Hunting Strategies
Welcome to the intriguing world of Abelisaurus, the fleet-footed predator of the Late Cretaceous period.
Unraveling the locomotion and hunting strategies provides insights into how this theropod survived in a world of giants.
Let’s embark on a prehistoric journey to compare Abelisaurus with other theropods, exploring their movement and predatory skills.
Bipedal Movement Across Theropods
Theropod dinosaurs, including Abelisaurus, famously walked on two legs. This posture made them fast and agile hunters on the ancient landscapes.
Bipedalism allowed these creatures to conserve energy while covering vast territories in search of food.
- Long hind limbs provided balance and speed
- Hollow bones and strong muscles helped in swift movements
- Bipedal design allowed for quick directional changes during chases.
Predatory Tactics And Potential Prey
Abelisaurus, a carnivorous contender in the Cretaceous ecosystem, used various hunting strategies.
Its keen senses and teeth designed for slicing through flesh suggest Abelisaurus was a top predator.
Fossils tell us that these dinosaurs may have preyed upon smaller animals and possibly scavenged when opportunities arose.
Potential prey included:
- Small herbivores: Easily overpowered.
- Dinosaurs with armored skin: Required strategic attacking.
- Other carnivores: Sometimes competitors turned into meals.
These hunting tactics and choices of prey highlight the adaptability of Abelisaurus among the diverse group of theropods.
Environmental Adaptation
Dinosaurs thrived millions of years ago, covering vast lands and diverse habitats. Each species, like the fierce Abelisaurus, adapted uniquely. Explore how this incredible theropod navigated its environment compared to its rivals.
Habitat Preferences Of Abelisaurus Versus Rivals
The Abelisaurus, a predator from the Late Cretaceous period, had unique habitat preferences. Unlike some competitors, this dinosaur favored areas with ample hiding spots. Dense forests and broken terrain were ideal for ambush attacks.
- Abelisaurus: Preferred dense woodlands for surprise hunts.
- Rivals: Some loved open plains for fast chases.
This contrast in habitat selection offered Abelisaurus an edge in environments where stealth was key.
Other carnivores had to rely on speed and endurance in open habitats, making this a pivotal factor in the survival of the Abelisaurus.
Survival Strategies In Changing Climates
As climates fluctuated, dinosaurs had to adapt or perish. The Abelisaurus displayed remarkable versatility. It changed its diet and hunting tactics to match the shifting conditions.
| Species | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Abelisaurus | Diversified prey to adapt to food availability |
| Other Theropods | Migrated to follow prey herds |
This strategic flexibility meant adapting to colder or warmer climates effectively. While Abelisaurus could alter its hunting style, rivals typically had to move to new territories.
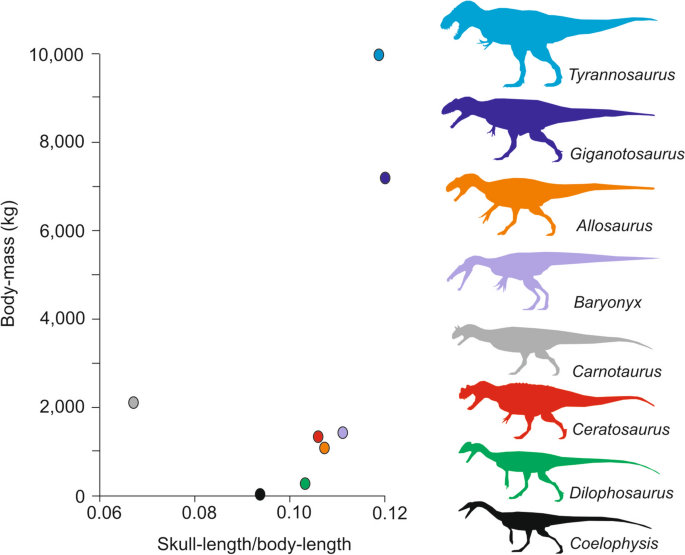
Credit: link.springer.com
Intelligence And Social Behavior
Understanding the intelligence and social behavior of dinosaurs such as Abelisaurus offers a glimpse into their world.
Comparing this intriguing theropod with its peers can shed light on its cognitive abilities and group dynamics.
Scientists use clues from fossils to make educated guesses about these behaviors. Let’s delve into the fascinating realm of Abelisaurus’s brainpower and communal life.
Brain Size And Cognition
Brain size can tell us much about a dinosaur’s smarts. A larger brain often means higher intelligence. Abelisaurus, like other theropods, had a relatively modest brain. Its brain size gives us hints about how it thought and acted.
- Small but complex: Abelisaurus’s brain was not big, but it was advanced for its time.
- Sensory abilities: Its brain supported good senses, such as sharp eyesight.
- Olfactory clues: A part of its brain was for smelling, hinting at strong scent detection.
Evidence Of Social Structure And Communication
Did Abelisaurus live and hunt in packs? Some clues suggest they might have had social structures.
- Tracks found together hint at group movement.
- Fossil beds show remains of many individuals in one place.
These finds can suggest that Abelisaurus communicated and perhaps worked as a team. They may have used calls or body language to talk to each other.
Fossil Evidence And Geographic Distribution
Fossil Evidence and Geographic Distribution offer crucial insights into the ancient world of the Abelisaurus. These captivating creatures roamed the earth during the Late Cretaceous period.
Paleontologists piece together their history via rare fossil remnants. Such evidence sheds light on their behavior, environment, and whereabouts millions of years ago.
Fossil Finds Around The World
The Abelisaurus, a fascinating genus of theropod dinosaurs, has an elusive fossil record. The majority of its known history is based on a partial skull found in Argentina.
Yet, this find cues a larger story of its existence and reign. Fossil evidence from various regions helps us understand the Abelisaurus’ expansion across continents.
- South America: The hotspot for Abelisaurus discoveries, with Argentina leading the cache of significant finds.
- Other Continents: Speculative evidence suggests that related species could extend their reach beyond the prehistoric Southern Hemisphere.
Reconstruction Of Migration And Range
Understanding Abelisaurus migration involves examining the continental drifts during the Cretaceous.
Fossils play a vital role; they tell us where these theropods may have traveled. Experts use sophisticated tools to trace these movements.
- Analyze fossil locations with ancient continental layouts.
- Contrast skeletal similarities among related dinosaur species.
- Infer possible land bridges or dispersal routes.
Research proposes that Abelisaurus may have roamed far and wide. Their adaptations indicate a possibility of varied habitats, from lush forests to arid deserts.
The incomplete fossil record, thus, provides a puzzle for continuous exploration and analysis by scientists.
| Location | Fossil Findings | Possible Range |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | Partial skull and skeletal fragments | Southern Gondwana |
| Potential | Comparative analysis of theropods | Extended areas of ancient supercontinents |
Extinction Factors
Understanding why Abelisaurus became extinct is crucial to learning about Earth’s past.
These giants vanished from our planet’s surface.
Many factors contributed to their disappearance. We examine the major elements that ended the era of Abelisaurus.
Cretaceous Mass Extinction And Abelisaurus
At the end of the Cretaceous period, a massive extinction event reshaped life on Earth.
The Abelisaurus, like many dinosaurs, fell victim to this event.
- A huge asteroid impact is a widely accepted cause.
- Dust and debris blocked sunlight, changing the climate.
- Plants died, followed by herbivores and then predators like Abelisaurus.
Competitive Pressures And Environmental Changes
Before the asteroid hit, Abelisaurus faced other challenges. The environment was changing. New competitors arose.
- Shifting continents altered habitats and food sources.
- Smaller, more efficient predators appeared, competing for food.
- Volcanic activity and temperature shifts added stress.
Cultural Impact And Public Fascination
Abelisaurus, a Late Cretaceous predator, stirs imagination across the globe. Once ruling ancient landscapes, its legacy continues to captivate audiences through various mediums.
The remarkable size and unique features of this theropod dinosaur make it a worthy subject of interest in the realms of media and education.
Abelisaurus In Media And Literature
Fascination with Abelisaurus permeates through books and screen. This towering dinosaur sparks intrigue, often featuring in dinosaur documentaries and children’s books. Its depiction in media offers an intriguing glimpse into its mysterious past.
Audiences are treated to thrilling portrayals that bridge the gap between ancient times and the present day.
- Documentaries: Showcase Abelisaurus in its natural habitat
- Fiction: Imagines thrilling encounters in novels and comics
- Children’s Literature: Introduces young minds to prehistoric wonders
Role In Education And Science Communication
The story of Abelisaurus is a springboard for educational journeys into the world of dinosaurs. Museums and science centers leverage its appeal for engaging storytelling. Lifelike models and interactive displays inspire learning in students of all ages.
Science communicators use Abelisaurus as a compelling character to illustrate scientific concepts and foster a deeper understanding of Earth’s history.
- Museum Exhibits: Offer awe-inspiring encounters
- Educational Programs: Provide hands-on learning experiences
- Academic Research: Fuels new discoveries and insights
What Made Abelisaurus Stand Out Among Other Late Cretaceous Theropod Dinosaurs?
Abelisaurus late cretaceous hunting abilities made it stand out among other late Cretaceous theropod dinosaurs. With its strong legs and sharp teeth, abelisaurus was a formidable predator. Its speed and agility allowed it to effectively hunt and catch its prey, establishing its dominance in the dinosaur kingdom.
Future Research Directions
The path to unraveling the mysteries of Abelisaurus is as thrilling as it is challenging. As paleontologists comb through ancient rocks, the quest to understand these extinct predators continues.
With advanced technologies at our disposal, the future looks bright for new insights into the Abelisaurus.
Here are some vital areas that hold much promise.
Unanswered Questions About Abelisaurus
This fascinating theropod leaves many pondering:
- What was its behavior?
- Why did it have such a powerful bite?
- Did its arms serve a special purpose?
Exploring these questions will shed light on its life millions of years ago.
Technologies Advancing Theropod Research
New tools are revolutionizing dinosaur studies:
- 3D scanning creates detailed models
- Isotopic analysis unveils feeding habits
- Computer simulations predict behavior
These technologies give new perspectives on the Abelisaurus.
Conclusion
In summing up the fascinating world of theropods, the Abelisaurus stands out for its unique features.
Our comparison shows that while it shares traits with other predators, it has its distinct place in prehistory.
Through careful study and continued fossil discoveries, our understanding of this captivating dinosaur will undoubtedly evolve.
Remember, the quest to learn more about these ancient creatures never goes extinct.