7 Tips on the Bipedal to Quadrupedal Shift
To shift smoothly from bipedal to quadrupedal movement, maintain core strength and flexibility. Gradually increase weight distribution across all limbs for balance.
Exploring the transition from bipedal to quadrupedal motion is a journey into the foundational aspects of human and animal locomotion.
This fascinating shift provides insights into the mechanics of movement that are not only useful for understanding the evolution of species but also for improving athletic performance and physical rehabilitation processes.
Embarking on the practice of moving on all fours can enhance coordination, strength, and stability, offering a myriad of benefits for those learning or perfecting the technique.
Here, we uncover seven pivotal tips to make this transformative journey from walking on two legs to navigating on all fours intuitive and efficient.
With a focus on key elements like body mechanics, gradual training adjustments, and postural alignment, anyone can approach this shift methodically and safely.

Evolving Posture: Biped To Quad
The journey from walking on two legs to four is a fascinating one. Many creatures, including some ancestors of humans, have made the shift from bipedal to quadrupedal locomotion.
This transition involves complex changes in anatomy and energy use. Let’s explore what this shift entails and why it might occur.
Anatomical Shifts Involved
Adapting to a quadrupedal lifestyle means big changes for the body. Here are the key anatomical shifts:
- Spinal changes: The spine evolves from an ‘S’ shaped curve to a more horizontal alignment.
- Limb reconfiguration: Arms and legs adapt for weight-bearing and efficient movement on all fours.
- Skull realignment: The position of the skull changes, affecting balance and field of vision.
- Muscle development: New muscle groups strengthen to support the quadrupedal posture.
These shifts aren’t quick or simple. They occur over generations through the process of natural selection.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
A shift in how a creature moves often comes down to energy. Moving on four legs can save energy.
Here’s why:
- Stability: Four points of contact provide a stable base, reducing the energy needed to balance.
- Endurance: Quadrupedal movement often uses less energy per distance traveled, allowing for longer treks.
- Speed: Many animals achieve faster speeds on four legs, making hunting or evasion more efficient.
Energy savings can lead to better survival odds. This often drives the evolution from bipedalism to quadrupedalism.
Beginner’s Guide To Quadrupedal Training
Are you curious about transforming your bipedal movements into a quadrupedal flow? This guide is perfect for starters.
In quadrupedal training, you simulate the movements of four-legged creatures, enhancing your strength, flexibility, and coordination. Before venturing on all fours, let’s break down some basic tips.
Starting With The Basics
Master the fundamental postures to avoid injury and gain the most from your training. Focus on these steps:
- Proper hand placement: Keep your hands under your shoulders.
- Even weight distribution: Balance your weight between your hands and feet.
- Neutral spine: Aim for a straight back to maintain a natural posture.
- Controlled breathing: Breathe deeply to increase your core stability.
Start with short sessions. Gradually increase the duration as your body adapts.
Progressive Overload Approach
Build your quadrupedal technique gradually to push your limits safely. Use the following guidelines:
- Increase the difficulty slowly over time.
- Add complexity with new movements once you’re comfortable with the basics.
- Track your progress to stay motivated.
Remember, consistency is key in quadrupedal training. Enjoy the journey as your body learns this unique way of moving!
Mastering Balance And Stability
The journey from bipedal to quadrupedal movement is not just about the physical shift.
It’s about understanding your body’s core, your limbs, and how they work together.
Steady and controlled movements define this transition.
To achieve this, focusing on balance and stability is key.
Let’s explore the essential techniques to enhance these elements.
Core Engagement Techniques
Your core is the foundation of all movement.
A strong core keeps you balanced. Start with these exercises:
- Planks: These strengthen the entire core.
- Side Planks: These target obliques which are crucial for lateral stability.
- Dead Bugs: Activate deep core muscles and coordinate limb movements.
Practice daily for best results. Use a mirror to check your form.
Keep your back flat and use your breath to power movements.
Stabilizing The Limbs
Stable limbs are vital for a smooth quadrupedal shift.
Begin with exercises that hone the muscles of your arms and legs:
- Squats: Build leg strength and improve joint stability.
- Push-ups: Develop arm and shoulder strength.
- Lunges: Enhance leg muscle balance and coordination.
Ensure proper alignment to prevent injury.
Focus on a full range of motion to promote joint health.
Include rest days to allow your muscles to recover.
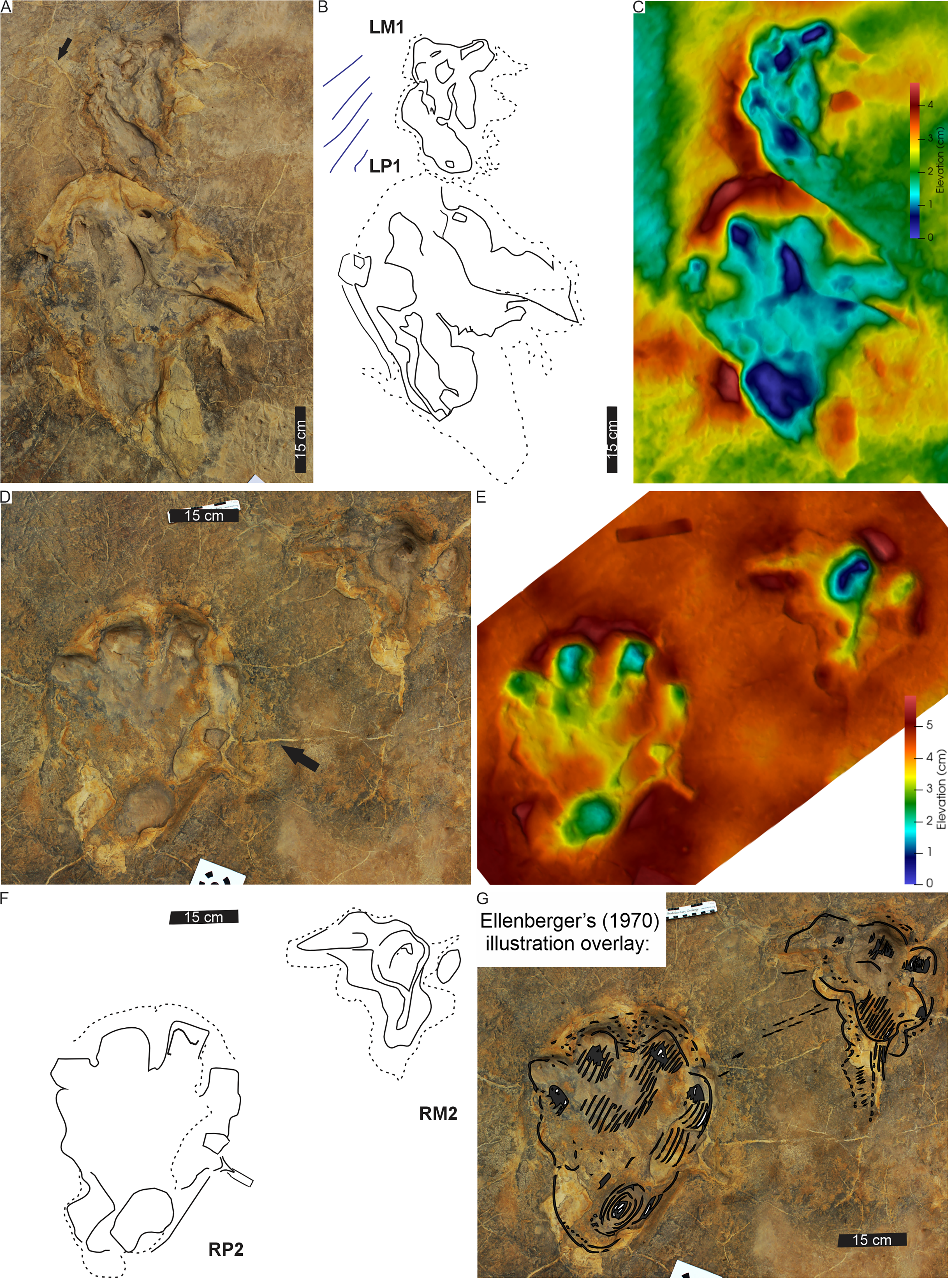
Credit: peerj.com
Strengthening Muscles For Transition
Strengthening Muscles for Transition is critical for anyone looking to shift from bipedal to quadrupedal movement.
This change requires core and limb muscles to adapt for new stressors. Preparing your body is essential for a smooth transition and to prevent injuries.
Targeting Key Muscle Groups
Targeting specific muscles helps build a strong foundation. Quadrupedal motion requires a robust core, flexible hips, and strong shoulders. Focus on exercises like planks for core, lunges for hips, and push-ups for shoulders.
- Core exercises – Planks, Russian twists, mountain climbers
- Hip flexors – Lunges, high knees, leg raises
- Shoulder stabilizers – Push-ups, arm circles, shoulder presses
Mixing Bipedal And Quadrupedal Exercises
Mixing exercises from both forms increases muscle readiness. Start with a bipedal exercise, like jogging, then shift to a quadrupedal one, such as bear crawls.
| Bipedal Exercise | Quadrupedal Exercise |
|---|---|
| Jogging | Bear Crawls |
| Squats | Frog Hops |
| Jumping Jacks | Crab Walks |
By alternating the exercises, your muscles can adapt more easily. Use a steady progression, increasing the difficulty as you gain strength.
Integrating Proprioceptive Training
Proprioceptive training is like giving your body a road map. It helps you understand where you are and how to move.
Think of it as your internal GPS. When shifting from walking on two legs to moving on all fours, this training is key. It can make the move smoother and safer.
Developing Spatial Awareness
Spatial awareness is knowing where your body parts are without looking. You can train for better awareness with specific exercises. These activities enhance your perception of space and body position.
- Blindfolded Obstacle Course: Move through a simple setup without sight. It forces you to trust your body’s senses.
- Barefoot Exploration: Walk barefoot on different surfaces. It improves foot sensitivity and body awareness.
Enhanced Motor Coordination Drills
Motor coordination drills make your movements smooth and efficient. They link your brain, body, and muscles in harmony.
| Drill | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Bear Crawls: | Move on hands and feet, keeping hips and shoulders level. | Teach even weight distribution. |
| Crab Walks: | Move on hands and feet, belly facing up. | Build core and limb coordination. |
Mobility Work For Fluid Movement
Imagine moving from standing on two legs to walking on all fours with ease. Bipedal to quadrupedal shift requires more than muscle strength. It demands high mobility. Let’s dive into exercises that improve movement fluidity.
Joint Flexibility Routines
Gaining flexibility in joints helps smooth transitions between postures. Think of hinges on a door. The better they move, the easier the door swings. The same goes for your joints.
Start with a warm-up to ready the joints. Warm muscles stretch better. Focus on hip and shoulder mobility. These areas are key in quadrupedal movement.
- Shoulder rolls loosen the upper body.
- Hip circles encourage lower body mobility.
Include yoga poses like Downward Dog and Cat-Cow. These poses work on full-body mobility.
Dynamic Stretching Benefits
Dynamic stretches prepare your body for movement. They mimic the action you’re about to do. This way, your body gets ready for the shift.
Dynamic stretching increases blood flow. It also boosts your range of motion. You’ll find the shift from bipedal to quadrupedal less taxing.
- Try leg swings to open up the hips.
- Do arm swings to activate shoulder joints.
Include these routines before any physical activity. They’re key for a smooth transition in movement patterns.
How did the evolutionary journey of Aardonyx influence the bipedal to quadrupedal shift?
The aardonyx pioneering sauropodomorph evolution sheds light on the transition from bipedal to quadrupedal movement in dinosaurs. This evolutionary journey provides insights into the development of locomotion and the anatomical changes that facilitated the shift in posture. Aardonyx’s fossil record offers valuable information on this crucial stage in dinosaur evolution.
Can the Bipedal to Quadrupedal Shift be Applied to Creating a Barney the Dinosaur Costume?
Yes, the bipedal to quadrupedal shift can be utilized to create a Barney the Dinosaur costume. By adjusting the design to allow for a more realistic and comfortable four-legged movement, the costume can accurately portray the beloved character while still being functional for the wearer.
Adapting To Different Terrains
Moving from two legs to four is a big change, especially on different terrains. Animals and robots that make this shift face new challenges.
They have to handle various ground types. This means changing the way they move. Let’s explore how they can adapt to tackle these challenges.
Varied Surface Challenges
Every surface is unique. Some are soft like sand, while others are hard like rock. Animals and robots must learn the textures. This helps them move better.
Here are tips for varied surfaces:
- Test the ground: Before moving, press down to see how the ground feels.
- Change the pace: On loose surfaces, move slowly. This stops them from slipping.
- Adjust the grip: Spread toes or widen wheels on slippery areas for better hold.
Overcoming Obstacles
Obstacles can be anything from rocks to logs. They require different skills to get past.
Here are some steps to overcome them:
- Scan ahead: Look for obstacles before reaching them. This helps plan the move.
- Choose a path: Find the easiest way around or over the obstacle.
- Use momentum: Keep moving to help get over something. Stopping can make it harder.
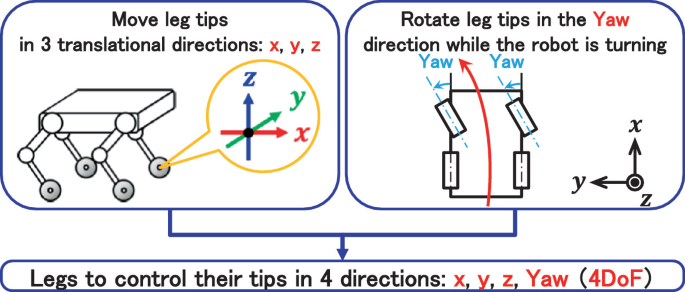
Credit: link.springer.com
Conclusion
Embracing the shift from two feet to four can unlock a new realm of mobility and strength. These seven tips guide that transition, enhancing your understanding and skill set.
As you integrate them, observe the changes in your posture, agility, and connection with your body’s natural movement patterns.
The journey to quadrupedal mastery is rewarding, so stay persistent and enjoy the transformation.






